Combining Histone Modification Therapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Tumor Treatment
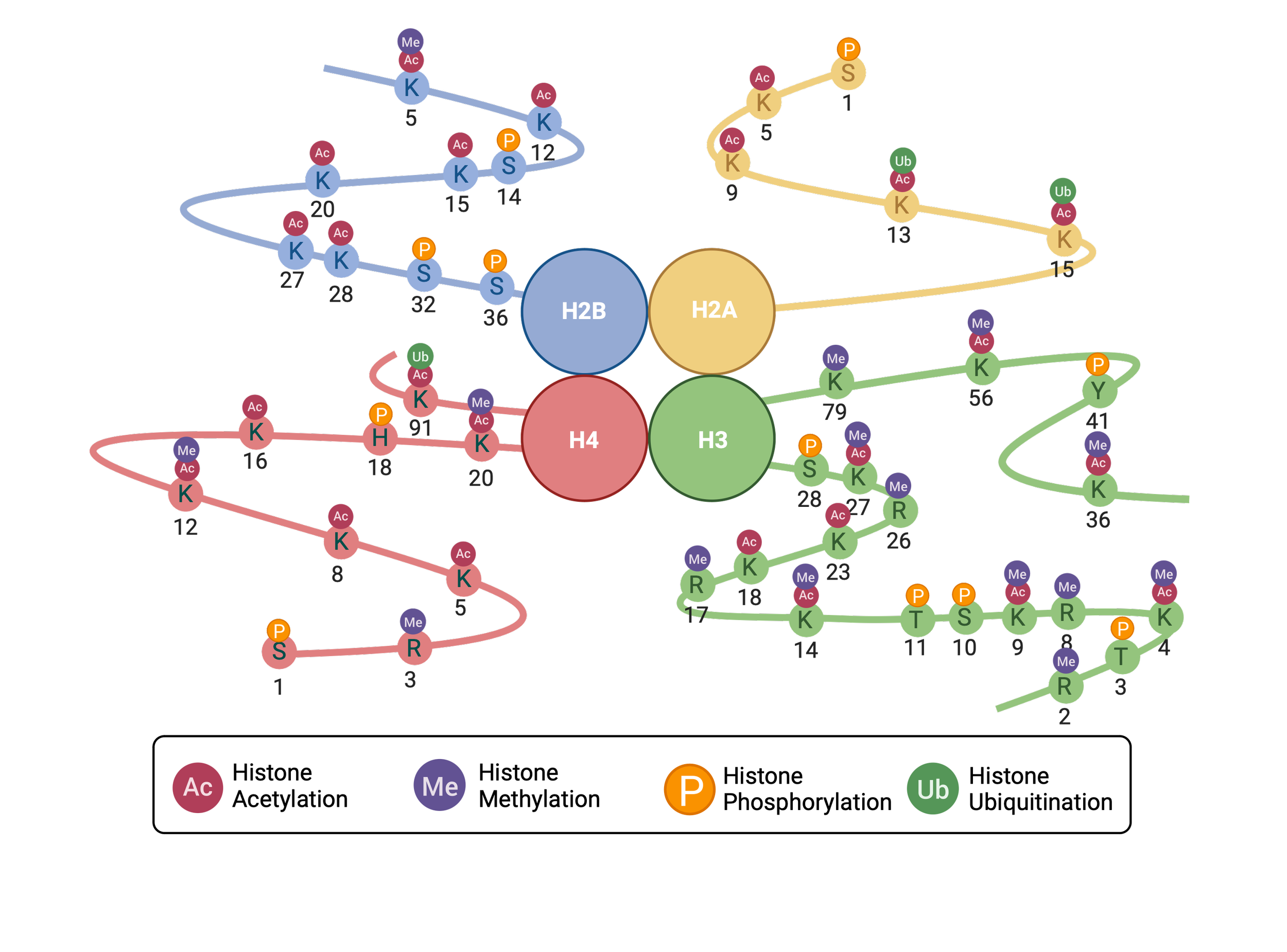
Overview of histone modifications involved in cancerogenesis. Various modulations could occur along the N-terminus tails of the four core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Modification marks consist of Ac (histone acetylation), Me (histone methylation), P (histone phosphorylation), and Ub (histone ubiquitination). Along the tails, certain amino acids can be modified more than once from different chemical groups, including H3K27ac/me, H3Kac/me, H4K91ac/ub, and H2AK13ac/ub.
Figure credit: original. Made in BioRender.com.
Full Research Paper
Wang, J. . (2024). Combining Histone Modification Therapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Tumor Treatment. Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology, 102, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.54097/xctrap38
Characterizing Treatments for Differentiated 5mC DNA Methylation on The APOE Gene in Coronary Heart Disease
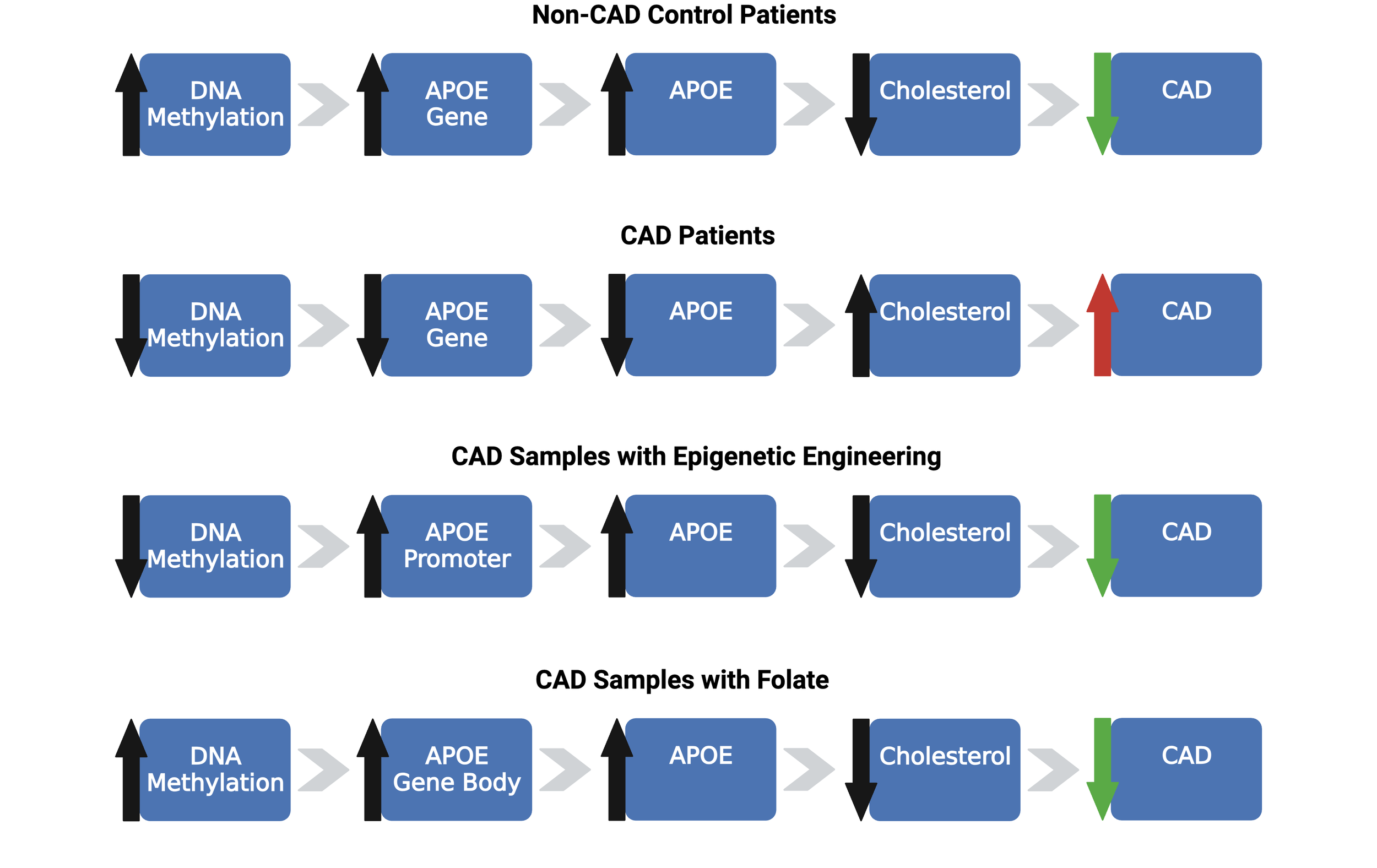
Overview of the predicted results under the condition that the grant proposal hypothesis holds true. By using modulation techniques, like CRISPR/Cas9, and increasing exposure to folic acid, DNA methylation levels will be predicted to increase, upregulating the APOE gene and elevating the APOE protein to manage cholesterol levels and prevent atherosclerosis.
Figure credit: original. Made in BioRender.com.
Investigating The Inverse Correlation Between Alzheimer’s Disease and Cancer
Overview of dysregulated mechanisms of the Wnt signaling pathway in cancer and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In the active Wnt pathway, GSK-3β (glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta) is inactivated, allowing β-catenin to accumulate and translocate to the nucleus, where it binds TCF/LEF transcription factors to promote the transcription of genes that drive cell proliferation and survival. Dysregulation of this pathway contributes to cancer by enhancing cell survival and uncontrolled growth. In the suppressed Wnt pathway, GSK-3β is active, leading to β-catenin degradation and the hyperphosphorylation of tau protein, a hallmark of AD pathology. This prevents the transcription of target genes necessary for cell survival, contributing to neuronal death.
Figure credit: original. Made in BioRender.com.